ACCESSO ALLA EEPROM NEI MICRO AVR
Scrittura ad un indirizzo specifico
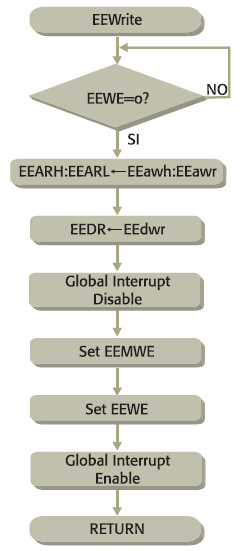
Il listato 1 presenta una routine per la scrittura in EEPROM ad uno specifico indirizzo. La routine EEWrite assume che in EEdwr vi sia il dato da scrivere, in EEawr e EEawrh rispettivamente la parte bassa e la parte alta dell’indirizzo a cui scrivere. In figura 1 il diagramma di flusso della routine. La routine occupa 9 words (oltre il return) e viene eseguita in 11 cicli (oltre il return) se la EEPROM è pronta.
.include “8515def.inc”
.def EEdwr =r16 ;data byte to write to EEPROM
.def EEawr =r17 ;address low byte to write to
.def EEawrh =r18 ;address high byte to write to
EEWrite:
sbic EECR,EEWE ;if EEWE not clear
rjmp EEWrite ;wait more
out EEARH,EEawrh ;output address high byte, remove if no high byte exists
out EEARL,EEawr ;output address low byte
out EEDR,EEdwr ;output data
cli ;disable global interrupts
sbi EECR,EEMWE ;set master write enable, remove if 90S1200 is used
sbi EECR,EEWE ;set EEPROM Write strobe
;This instruction takes 4 clock cycles since
;it halts the CPU for two clock cycles
sei ;enable global interrupts
ret
| Listato 1 |
Lettura da indirizzo specifico
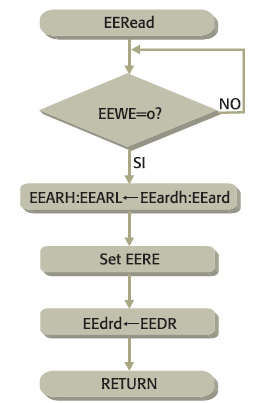
Nel listato 2 è riportata la routine per la lettura di un dato da uno specifico indirizzo in EEPROM. La parte bassa e la parte alta dell’indirizzo devono essere contenute rispettivamente nei registri EEard ed EEardh. La routine è composta da 6 word e viene eseguita in 7 cicli. Il diagramma di flusso è riportato in figura 2.
.include “8515def.inc”
.def EEdrd =r0 ;result data byte
.def EEard =r17 ;address low to read from
.def EEardh =r18 ;address high to read from
EERead:
sbic EECR,EEWE ;if EEWE not clear
rjmp EERead ;wait more
out EEARH,EEardh ;output address high byte, remove if no high byte exists
out EEARL,EEard ;output address low byte
sbi EECR,EERE ;set EEPROM Read strobe
;This instruction takes 4 clock cycles since
;it halts the CPU for two clock cycles
in EEdrd,EEDR ;get data
ret
| Listato 2 |
Scrittura sequenziale
La routine per la scrittura in EEPROM ad indirizzi sequenziali è riportata in figura 3 e il relativo codice nel listato 3. Il registro EEdwr_s deve contenere il dato da scrivere. La routine occupa 12 words e viene eseguita in 15 cicli.
.def EEwtmp =r24 ;temporary storage of address low byte
.def EEwtmph =r25 ;temporary storage of address high byte
.def EEdwr_s =r18 ;data to write
EEWrite_seq:
sbic EECR,EEWE ;if EEWE not clear
rjmp EEWrite_seq ;wait more
in EEwtmp,EEARL ;get address low byte
in EEwtmph,EEARH ;get address high byte, remove if no high byte exists
adiw EEwtmp,0x01 ;increment address
out EEARL,EEwtmp ;output address low byte
out EEARH,EEwtmph ;output address byte, remove if no high byte exists
out EEDR,EEdwr_s ;output data
cli ;disable global interrupts
sbi EECR,EEMWE ;set master write enable, remove if 90S1200 is used
sbi EECR,EEWE ;set EEPROM Write strobe
;This instruction takes 4 clock cycles since
;it halts the CPU for two clock cycles
sei ;enable global interrupts
ret
| Listato 3 |
Lettura sequenziale
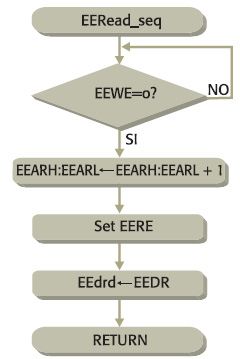
Per la lettura sequenziale di dati dalla EEPROM si può usare la routine di figura 4 il cui codice è riportato nel listato 4. Il dato letto viene posto in EEdrd_s. La routine è composta da 9 words e viene eseguita in 13 cicli.
.def EErtmp =r24 ;temporary storage of low address
.def EErtmph =r25 ;temporary storage of high address
.def EEdrd_s =r0 ;result data byte
EERead_seq:
sbic EECR,EEWE ;if EEWE not clear
rjmp EERead_seq ; wait more
; The above sequence for EEWE = 0 can be skipped if no write is initiated.
; Read sequence
in EErtmp,EEARL ;get address low byte
in EErtmph,EEARH ;get address high byte, remove if no high byte
exists
adiw EErtmp,0x01 ;increment address
out EEARL,EErtmp ;output address low byte
out EEARH,EErtmph ;output address high byte, remove if no high
byte exists
sbi EECR,EERE ;set EEPROM Read strobe
;This instruction takes 4 clock cycles since
;it halts the CPU for two clock cycles
in EEdrd_s,EEDR ;get data
ret
| Listato 4 |






Ottimi listati che un programmatore assembler (o assembly) dovrebbe avere nella propria libreria.